Agrivoltaics
Agrivoltaics combines the agricultural land use with the production of renewable photovoltaic electricity. It allows for production of food crops and electricity generation at the same time, under consideration of soil protection and water savings.
What is Agrivoltaics?
Agrivoltaics utilizes specific solar arrays in combination with certain agricultural practices based on region and climate. This creates a symbiotic relationship between solar power and agriculture, allowing both to flourish while optimizing land use.
Today, we see Agrivoltaics being applied worldwide in incredibly different and innovative ways. In some areas, agrivoltaics is already a well-established technology. However, the concept is still widely unknown in countries like the United States, with very few applications. Sandbox Solar helping to change that fact! Alongside our partners, we installed multiple agrivoltaic arrays in the last two years here in Northern Colorado, while gathering and providing research for further deployment of the technology nationwide!
We are proud to be a part of the growth of Agrivoltaics in North America and excited about its effects on a more self-sufficient future.
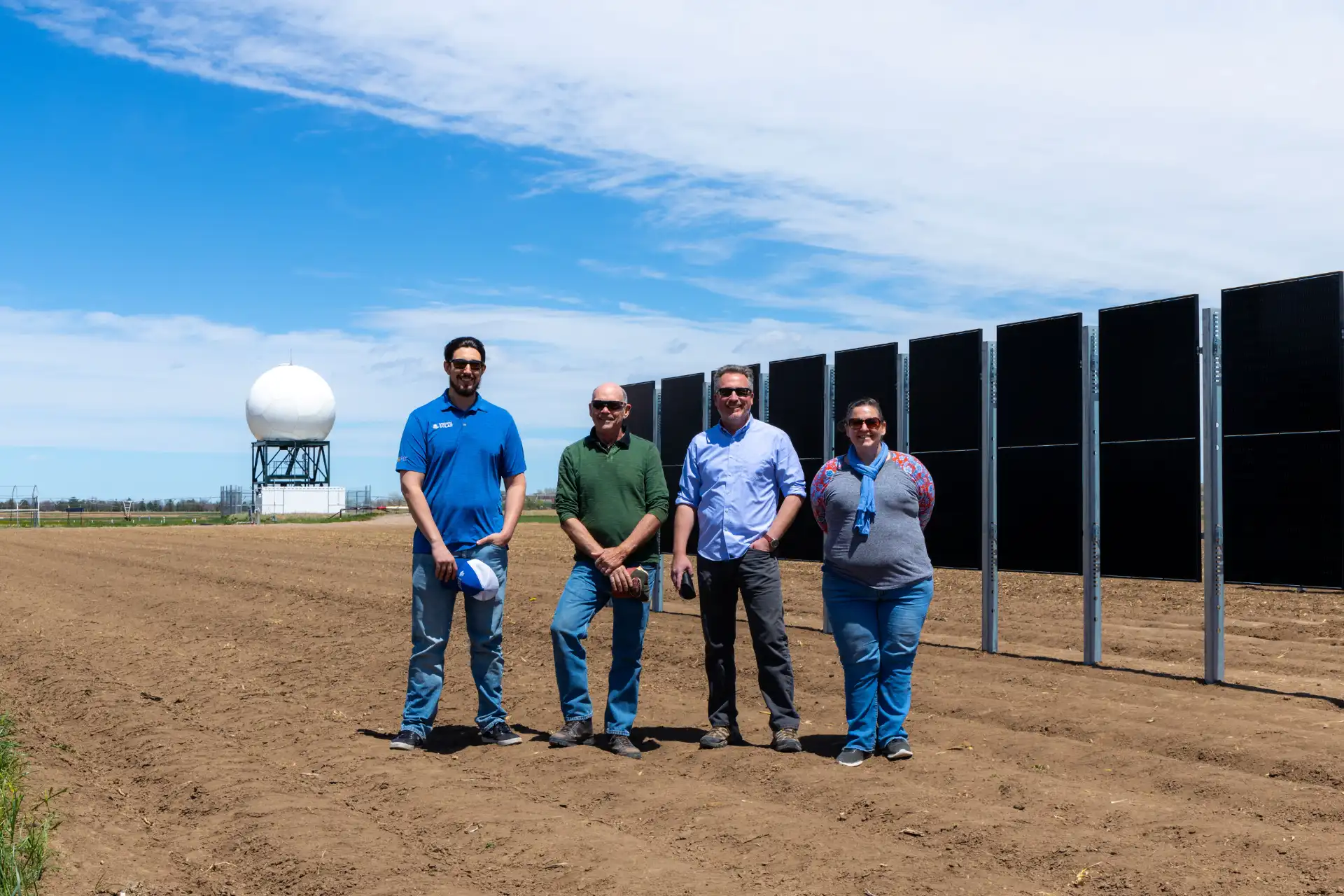
Sandbox Solar AGrivoltaics TEsting Grounds at CSU
Sandbox Solar, Colorado State University, and other solar partners teamed up to create our very own Agrivoltaics Testing Grounds at CSU’s ARDEC South. With funding from the Colorado Department of Agriculture, this plot will be used for research and educational purposes for further deployment of Agrivoltaics nationwide.
Click the button below to see live data being produced by the different arrays (different data points will be added as when received)
Agrivoltaics Mini Documentary
Agrivoltaics, a novel approach combining agriculture and renewable energy, addresses food security and energy challenges without harming the environment. Adaptable to local contexts, it includes strategies like elevated solar panels in Kenya improving crop yields, and vertical systems in Norway preserving forests. Agrivoltaics promotes sustainable energy and enhances agriculture, potentially redefining land use, energy, and food production.
In this mini documentary, ‘Reharvesting the Sun‘ by RE:TV, Sandbox Solar had some of its recent projects (listed below) featured as major developments towards achieving this goal.
AGRIVOLTAIC ARRAY TYPES
Agrivoltaics is agriculture + photovoltaics, there is no “one way” that agrivoltaics works best. There are multiple variables involved to make an informed decision on what type of agrivoltaics array you would like to install. Variables that include, climate, crop type, sun exposure, agriculture practices, and the space available for such arrays.
Check out our software SPADE to create an agrivoltaics array that right for you!
Bifacial Solar Fence Agrivoltaics
Spring Hill Greens is a local Fort Collins farm that strives to be entirely carbon-neutral. So naturally, they would need an extensive solar system to generate sufficient power for their entire farm to be energy self-sufficient. However, Spring Hill Greens required more land to support a conventional ground-mount solar array. What they needed was an agrivoltaic solution. So they called their local agrivoltaic solar company, Sandbox Solar.
Transparent Agrivoltaic Array
Sandbox Solar has an ongoing agrivoltaic research project in partnership with the Colorado State University Research Farm at ARDEC South. Thanks to funding secured from the USDA SBIR grant, Sandbox Solar was able to install 9 separate agrivoltaic arrays. These arrays test certain crop types with varying solar panel transparency to measure the results. Sandbox Solar and the CSU Department of Agriculture utilize this research for educational and practical implementation.
Mobile Agrivoltaics Array
This Native Hill Farms solar agrivoltaic array is quite unique! Our local farmers wanted a way to integrate enough solar to power their entire farm but could not find a way without sacrificing precious fertile farming land! We custom built this array to be able to slide beneath their green house allowing to them to transfer the area from one plot to another. By working with their existing agricultural practices we found a way to integrate solar in an efficient and innovative way.
ROOFTOP AGRIVOLTAIC RESEARCH
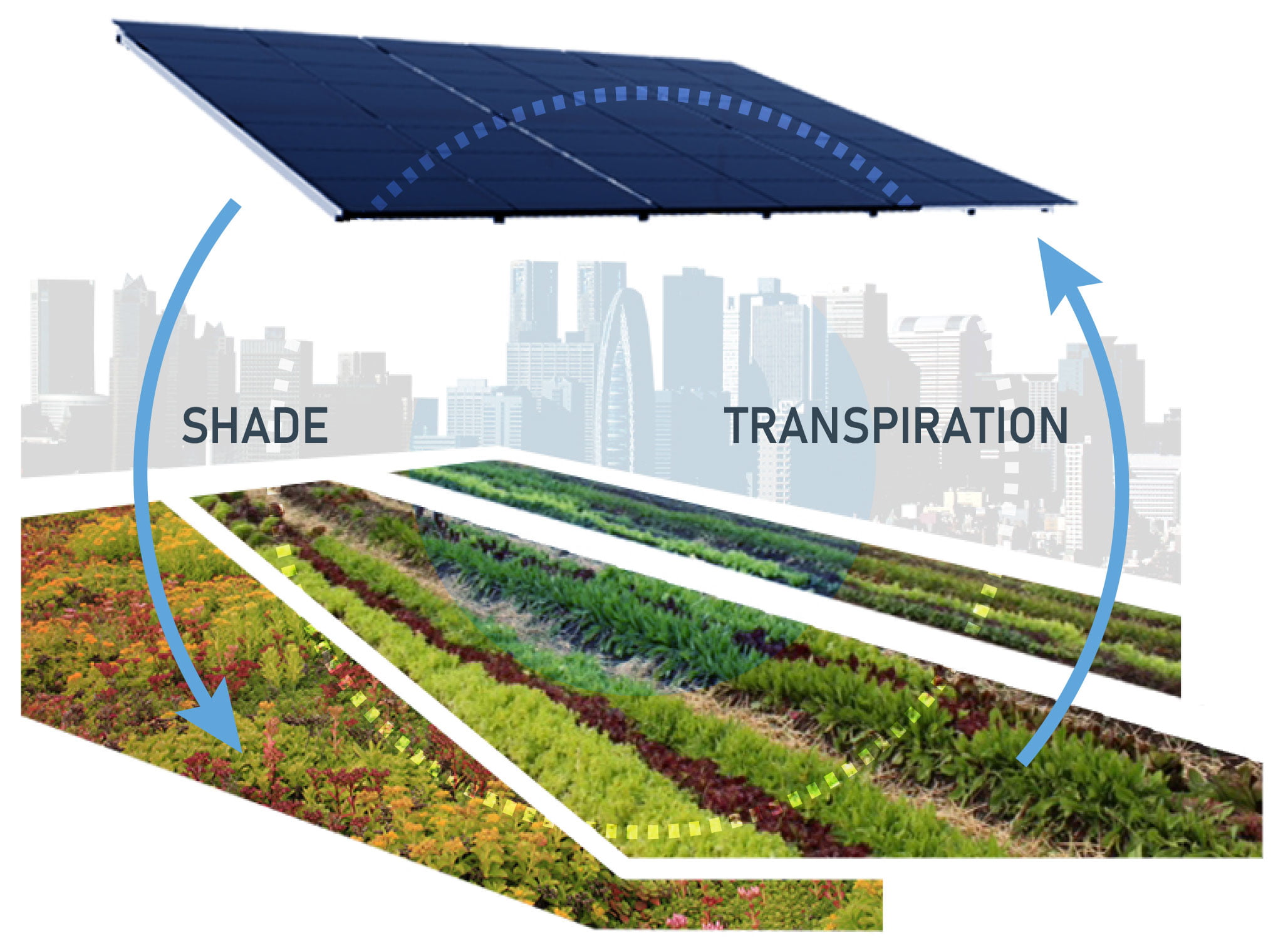
Rooftop agrivoltaics is the co-location of solar panels (photovoltaics) and food production on rooftops. Combining green roofs with rooftop solar is still in its infancy, but these systems’ synergies are well documented. The plants benefit from the solar panels’ protection, and panel performance improves on warm days due to the evaporative cooling that the plants provide. Agrivoltaic systems are currently used in farm fields but taking this concept to a rooftop is still unique.
With an increasingly urban population worldwide, having a hyper-local food source on the only remaining available space in urban areas, rooftops, can improve urban populations’ resilience – especially in times of crisis when food distribution chains may be disrupted. Renewable energy generation onsite also contributes to a more sustainable urban community, especially as non-renewable energy sources begin to decline. Educate yourself on the benefits and synergies of green roofs, ask your local government and energy providers how they support rooftop agrivoltaics, and seek out local food sources to help this emerging technology.
THE SYNERGY OF ROOFTOP AGRIVOLTAICS
- Shade from raised solar modules can project green roof plants species or edible plants from the harsh and exposed conditions that exist on rooftops.
- Transpiration from the plants rises to cool the bottom side of the solar modules, allowing them to operate more efficiently throughout the summer growing season.
AGRIVOLTAICS AT TED
TEDx ROOFTOP AGPV – Dr. Bousselot
- Over 50% of the world’s population lives in urban settings
- There is enough roof space in the City of Denver to produce 5 million pounds of food
- Green Roofs are “water limited” systems
- Solar panels provide a unique growing environment:
- Cooler in the Summer / Warmer in the Winter
- Less wind / Higher soil moisture
- Less sunlight = Less harmful UV radiation
- Solar (PV) panels benefit operate more efficiently with plants underneath
- Buy Local Food!
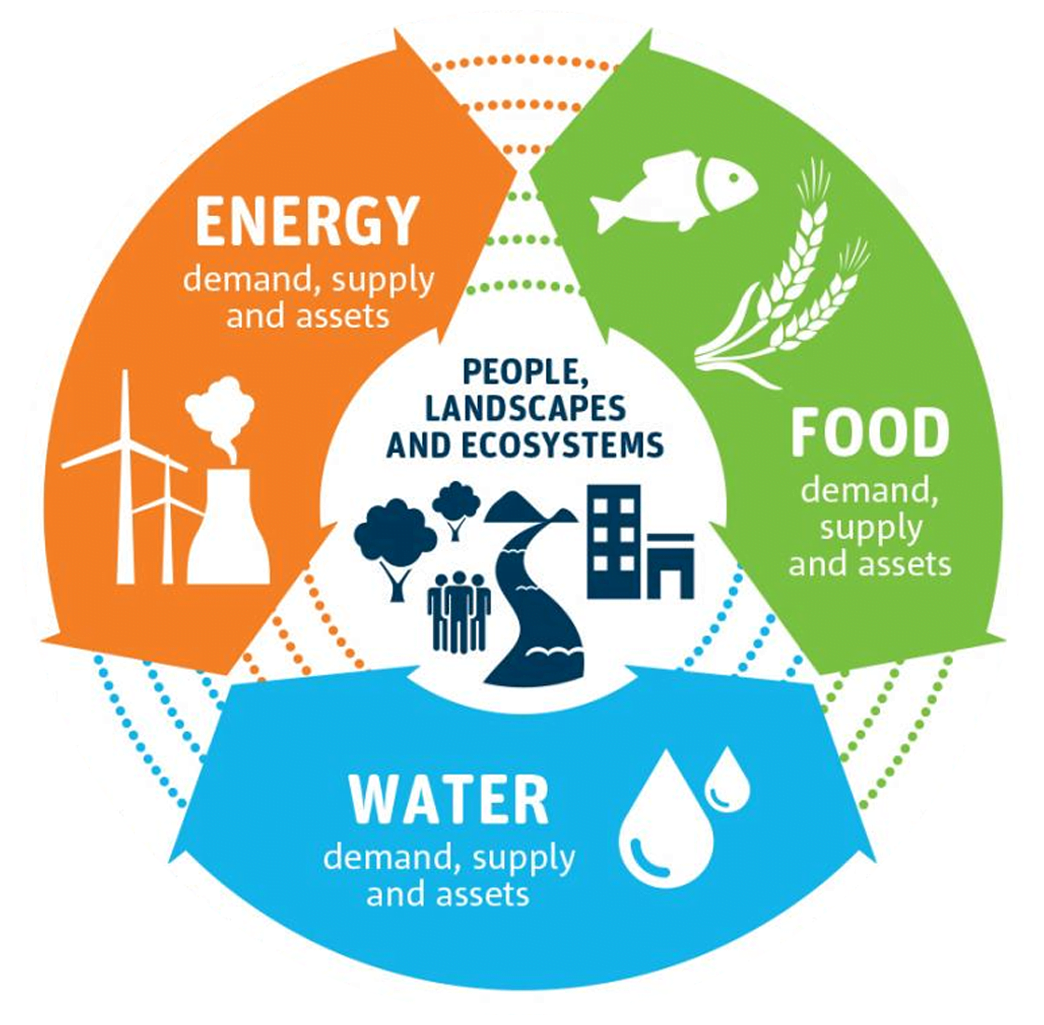
FOOD-ENERGY-WATER
The FEW nexus is the intersection of food, energy, and water, three interdependent components that, together, are the lifeblood of the Earth. By 2025, there will be nine billion people on Earth. Unless we are able to thoroughly understand the connection between all three, global efforts to meet the needs of people on Earth will fail.
In this sense, the FEW nexus affects everybody, from government, to industry, to academia, to citizens across the globe.
FOOD
Keeping agricultural lands in production & maintaining access to sustainable and nutritious food.
ENERGY
Supplying the demand for renewable energy demand for a growing population in urban and rural regions of the world.
WATER
Reducing water consumption & maintaining clean water access for a growing population.